By Kiana Cardeno, Nica Rhiana Hanopol, JM Casino, Ferdin Sanchez
(Part one of three)
The House of Representatives (HOR) is hardly representative.
In not so many words, a non-representative HOR is the reason for the enactment of the Party-list System Act in 1995 and the first party-list election held three years after. No less than the framers of the 1987 Constitution saw the need to establish a party-list system to ensure representation of the marginalized and underrepresented.
While its 2001 decision helped define what is meant by marginalized and underrepresented, the Supreme Court practically reversed itself 12 years later. On April 5, 2013, the highest court of the land decided that party-list groups do not need to represent any marginalized or underrepresented sector.
“In effect, anyone actually by that decision can join the party-list,” said Alicor Panao, a researcher on party-list systems and a political science professor from the University of the Philippines (UP) Diliman.
From two dominant parties in the 1950s, Nacionalista Party and Liberal Party, Republic Act (RA) 7941, or the Party-list System Act, sought to provide the broadest possible representation for the Filipino people, most especially the poor and marginalized.
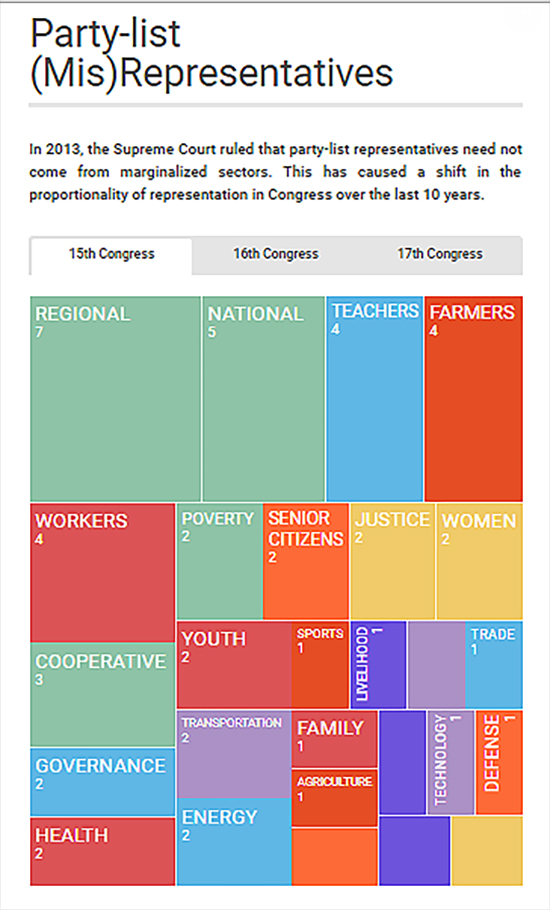
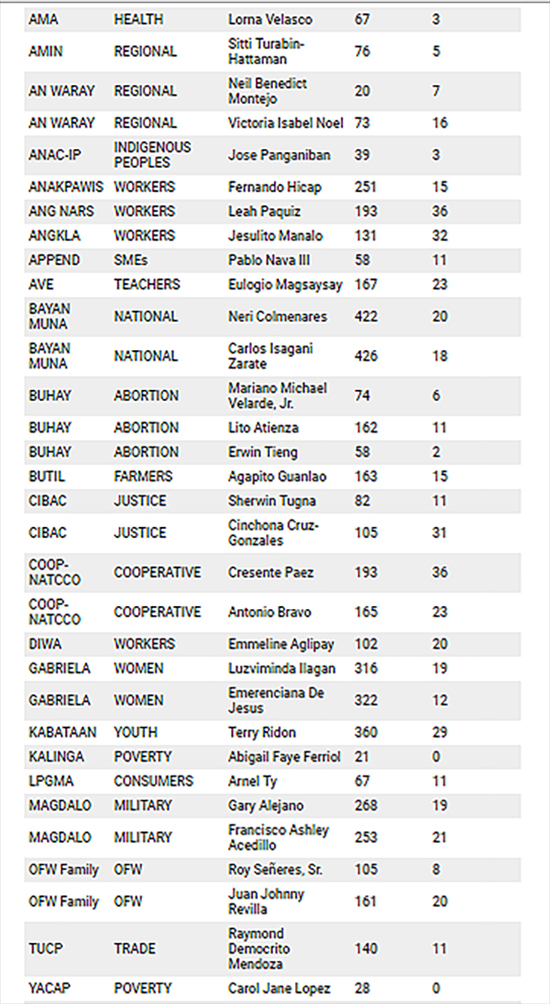
Over the last decade, the trends of proportionality in the House of Representatives have favored regional and workers groups, holding the most number of seats.
At present, more than 40 of active party-lists are now seated in Congress supposedly on behalf of laborers, peasants, fisherfolk, urban poor, indigenous cultural communities, elderly, handicapped, women, youth, veterans, overseas workers, and professionals.
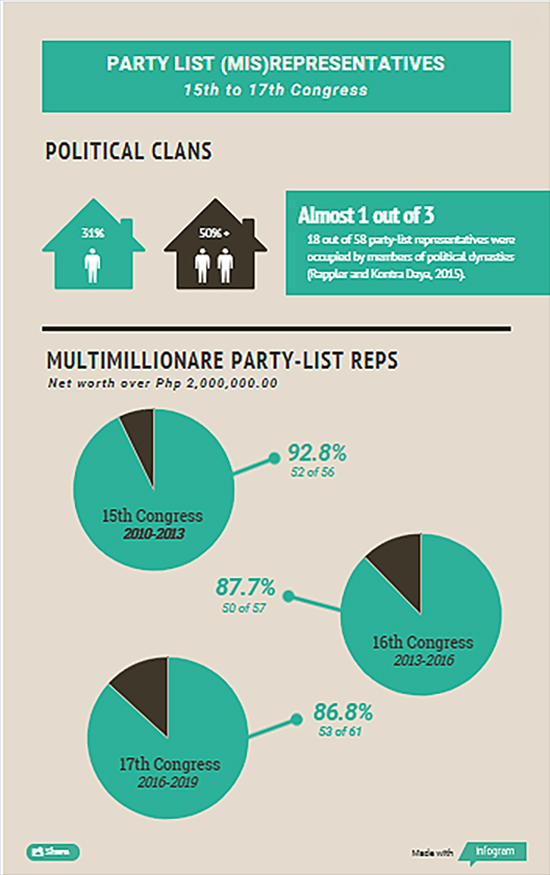
Many of those claiming to represent these marginalized sectors do not belong to these sectors and are members of well-entrenched political dynasties and special interest groups. Some have been implicated in corruption investigations while others have been known to promote special business interests. They are among the 59 party-list representatives occupying seats in Congress today.
Contradicting Actions
Some party-list representatives have been exhibiting contradicting platforms and have backgrounds that oppose what their party supposedly stands for.
1-PACMAN, a party geared toward supporting “marginalized nationals,” is represented by Michael Romero, who is a high-profile industrialist with a net worth of P7.2 billion, according to his Statements of Assets, Liabilities, and Net Worth (SALN) in 2017. He is also the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of several corporations such as Mikro-tech Capital, Inc, Harbour Centre Port Holdings, Inc., 168 Ferrum Pacific Mining Corp., Manila North Harbour Port, Inc., and GlobalPort 900 Inc. An author and co-author of 473 bills, only four of these may be classified as poverty alleviation.
Similar to Romero, Rep. Rico Geron of AGAP party-list is a multi-millionaire who claims to represent agricultural workers. He is the former chief executive officer (CEO) of Sorosoro Ibaba Development Cooperative (SIDC), one of the largest agricultural cooperatives in the country. In 2016, SIDC’s employees went on strike citing unjust labor policies like low pay and contractualization. That year, Pagkakaisa ng Manggagawa sa Timog Katagalugan (Pamantik-KMU) condemned the “anti-worker nature” of Geron and his party-list group.
Meanwhile, other party-list representatives have also been accused misdeeds.
Incumbent Rep. Arnel Ty of LPGMA or the LPG Marketers Association, a party-list that advocates “the need of the consuming public to have access to lower-priced LPG,” was found guilty of the unauthorized refilling of branded LPG tanks belonging to oil companies, violating Batas Pambansa Blg. 33 or “short selling and adulteration of petroleum and petroleum products” in 2016.
Along with former Agriculture Secretary Proceso Alcala, incumbent AGRI Rep. and garlic trader Orestes Salon faced graft charges filed by the Office of the Ombudsman. Salon and his 23 co-accused were allegedly able to monopolize the supply of garlic during the Aquino administration, manipulating the prices of garlic from 2010 to 2014.
Salon, who supposedly champions the rights of farmers in the country, posted a bail of P30,000 for his alleged involvement in the garlic cartel.
Ang Mata’y Alagaan (MATA) party-list claims to represent the blind and visually impaired. Also engaged with the overall health of the Filipino, the group also claims to give away free medicine, consultations, operations, and dental missions. However, MATA party-list Rep. Tricia Velasco-Catera is the daughter of retired SC Justice Presbitero Velasco and re-electionist Torrijos Mayor Lorna Velasco. The former Supreme Court justice is now running as governor of Marinduque. Tricia’s brother Lord Allan Jay Velasco is running for congressional re-election. Ethics complaints were filed against Velasco-Catera over her alleged “highly unethical activities,” such as Gluta-drip sessions at her office in the House of Representatives during working hours.
Pinoy Aksyon for Governance and Environment (Page) said that the use of Glutathione drips is highly discouraged by established medical professionals. As reported by Rappler, Page questioned whether Velasco-Catera’s practice was safe or legal under the code of ethics for doctors, especially for having the Gluta-drip sessions inside her office. “One’s office cannot be considered a medical clinic. We do not want to even consider the dire consequences if something untoward happens to Rep. Catera in the very premises of the House of Representatives due to such unregulated practice of medicine,” Page said.
History of Disqualifications
In October 2012, Ang Galing Pinoy (AGP) was disqualified from the 2013 elections for failing to meet requirements on representation. They were among the 54 party-list groups and organizations that were barred from participating in the said elections. The Commission on Elections (Comelec) disqualified AGP because its nominees “did not represent its chosen marginalized sectors.”
Panao said that it is important to look at these political parties internally, specifically on the lack of proper guidelines on how nominees are chosen. He said that once a party successfully meets the qualifications set, they basically already have the freedom to choose whoever their nominee is, as long as they achieve the bare minimum. “If people elect [them], it can happen na yung mga nominee ay member ng political dynasty, member ng traditional or outterm, former district representative. So, pwede siyang gamiting backdoor.”
AGP aimed to represent the interests of such sectors as security guards, tricycle drivers, FX drivers, taxi drivers, and street vendors. One of AGP’s principal nominees was Juan Miguel “Mikey” Arroyo, son of former president Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo and was neither a security guard nor tricycle driver. At the time, the younger Arroyo was facing inquiries regarding his wealth, which by some reports increased from P5.7 million in 2001 to P101.3 million in 2009.
Following the 2013 SC decision, AGP was one of the party-list groups whose cases were not remanded to Comelec and remained disqualified. Furthermore, even after the SC decision, they decided not to appeal. AGP was then removed from the 2013 ballots, concluding with finality that they were not permitted to run in that year’s midterm elections.
A Backdoor Entry
Six years after the Atong Paglaum case, the party-list system has cemented itself as a backdoor entry for traditional politics in the already elite-dominated House of Representatives.
In 2012, the Comelec initiated special proceedings that sought the disqualification of several partylist groups after public outcry over the proliferation of nominees who were neither marginalized nor underrepresented. Groups like Kontra Daya filed disqualification cases against what they described as “fake” or non-marginalized partylist groups.
The groups disqualified by the Comelec soon brought their case to the Supreme Court. With the consolidation of 54 petitions from 52 party-list groups in 2013, the SC was prompted to decide on Comelec’s disqualification case against various groups from running in the May elections of the same year.
Among the most common grounds that Comelec cited for the disqualifications were:
1. The sector the party-lists aimed to represent were neither marginalized nor underrepresented
2. The nominees did not belong to those sectors
3. The nominees / political parties did not have extended histories in supporting their chosen sectors
A number of the grounds for disqualification were essentially rendered null by the SC decision, which set six new parameters to which the Comelec must adhere in determining who was allowed to participate in the May 2013 elections. The decision’s fourth parameter states that “it is enough that the party-lists’ principal advocacy pertains to the special interests and concerns of the sector.”
Renato Reyes, secretary-general of Bagong Alyansang Makabayan (BAYAN), said that this results in narrower representation, especially when measuring who gets to sit. “Mas-kumikitid yung representation… kasi yung party-list sana would have allowed other sectors to be represented. Pero yung mga dati nang nakaupo, gusto nila pati iyong partylist i-claim nila, hawakan nila, because it helps concentrate power in the hands of a few.”
While disadvantaged groups have their own seats, the law in its current form does not protect them from unfair competition, according to Reyes. “Ang dilemma is how can they compete during the elections doon sa mga dynastic party-list groups, tsaka sa mga well-funded local machineries? So yung mga party-list groups na talagang galing sa mga mahihirap yung kanilang kinatawan, lagi silang mahihirapang mag-compete and manalo ‘pag ang kalaban nga nila yung mga dynasties at yung mga bilyonaryo.”
Meanwhile, Panao said that the low requirement of only two percent to gain seats, albeit limited to three, also results in almost identical parties. “Hindi sila ganun ka-productive kasi hindi sila maka-forge ng alliance… hindi sila nagtutulungan kasi ine-alienate mo na no’ng kampanya ninyo; nagkaroon ng fragmentation sa halip na unity. Parties are meant to unify your preferences, that’s the point of party-list, whether you like it or not.”
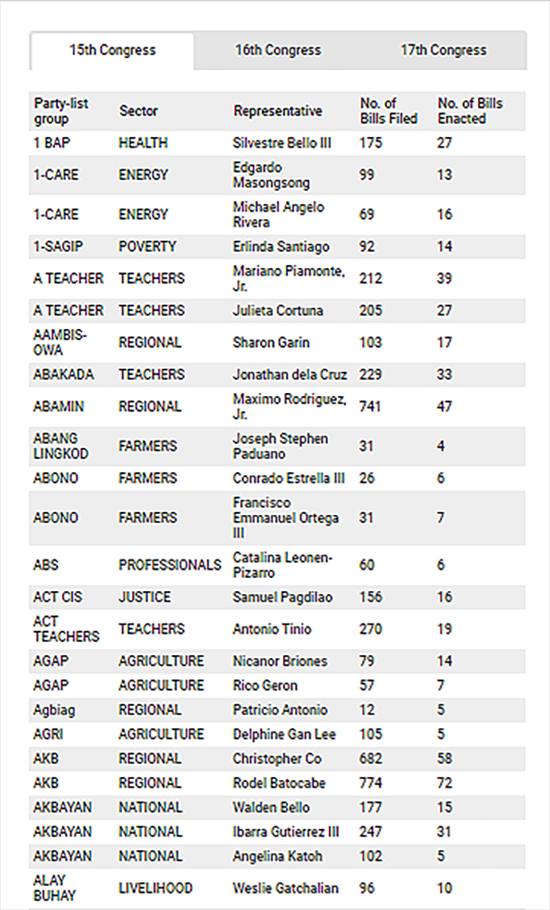
In the 17th congress, Kalinga Party-list, whose nominee is one of the poorest in Congress, was only able to file a total of 40 bills, whereas Ako Bicol Party-list, which listed multi-millionaires Christopher Co and Rodel Batocabe, filed 1,163 bills.
Despite the high number of bills authored and co-authored by Ako Bicol, only 55 unique bills were passed into law. The party-list was the main sponsor of 39 of these bills, and a co-sponsor of 16. These laws, however, were not directly concerned with the welfare of Bicolanos, the region they claim to represent.
In his statement in an interview with ABS-CBN, the late Ako Bicol Rep. Rodel Batocabe said that authoring bills that would only benefit Bicol would be “tantamount to class legislation and a violation of the equal protection clause of the constitution.”
“Amend it or craft a new law that defines with lesser ambiguity – with no ambiguity – those gray portions and those gray areas of the law. Ang nangyayari sa akin ngayon we have the law, we don’t amend it, and we let the Supreme Court do the interpretation,” Panao said. #
(Part 2: Party-list groups: Family Enterprise)