Putting Back the “Community” in Community Pantry
By L. S. Mendizabal
On the seventh day since the first community pantry on Maginhawa St., Quezon City was erected, one of its initiators, Ana Patricia Non, took a break but did not rest. The 26-year-old small entrepreneur, “Patreng” to many, gave a press conference via Facebook Live, explaining why she and her fellow organizers ceased operations temporarily: They did not feel safe after the National Task Force to End Local Communist Armed Conflict accused her of being a “communist,” a brand the Duterte administration has proclaimed to be synonymous with “criminal,” “terrorist,” “a menace to society.”
“People are grateful because the community pantry revived their spirits to help one another in times of crisis . . . But even that had to stop. It hurts that we were forced to close even for just a day. Think of how many families, how many meals the community pantry would have provided,” Patreng said in Filipino, her voice cracking, barely able to hold back tears. “We had to stop for the time being to ensure our safety and to clear the allegations.”
On the same day, Metro Manila Eastern Police District set up its own community pantry with rice, canned goods, face masks and face shields. Also stacked are copies of the Gideon Bible and the police journal magazine replete with red-tagging propaganda because, y’know, “Communism is bad.” Throughout the Duterte regime alone, PNP is notorious for tens of thousands of extrajudicial killings in the war against drugs and anti-terror campaign. From accessorizing dead bodies with pieces of cardboard that said, “Pusher ako, huwag tularan (I am a drug pusher, do not emulate)” to giving away food and bibles under cardboard signs stating a rather interesting iteration of the Maginhawa Community Pantry slogan,
“Magbigay nang naaayon sa kakayahan, dumampot ayon sa inyong pangangailangan (Give what you can, seize what you need)”—their altruism is of the violent kind.

Death, hunger, gloom and doom
Since the novel coronavirus claimed its first victim in the Philippines when the government failed to promptly close our borders, there’s been no mass testing or contact tracing. Hospitals are full. Frontliners are grossly underpaid, overworked and dying. COVID funds amounting to a trillion pesos have yet to be felt by 18 million beneficiaries still waiting for a second cash dole-out.
Unemployment is at an all-time record high. According to IBON Foundation, the total number of unemployed and underemployed soared to a staggering 12 million in February 2021. With the absence of food subsidy and the disruption of food systems, the poor are the hardest hit by draconian lockdowns, or this administration’s single palpable response to the pandemic. Minimum wage earners must go out to work or find work every day, risking COVID exposure. Staying home is a luxury the poor simply can’t afford. To them, dying from hunger is a more immediate concern than dying from the virus.
Academics of the Philippine Sociological Society in a study on the community pantry initiative claim that Filipinos have also been experiencing feelings of “gloom and doom.” WHO says that isolation, bereavement, fear and loss of income during the pandemic have been detrimental to individual mental health. Constant news of human rights violations may cause gloom and doom as well, for how can you sleep soundly at night knowing a 12-year-old boy just died after barangay tanods chased him when he was “caught playing outside?”
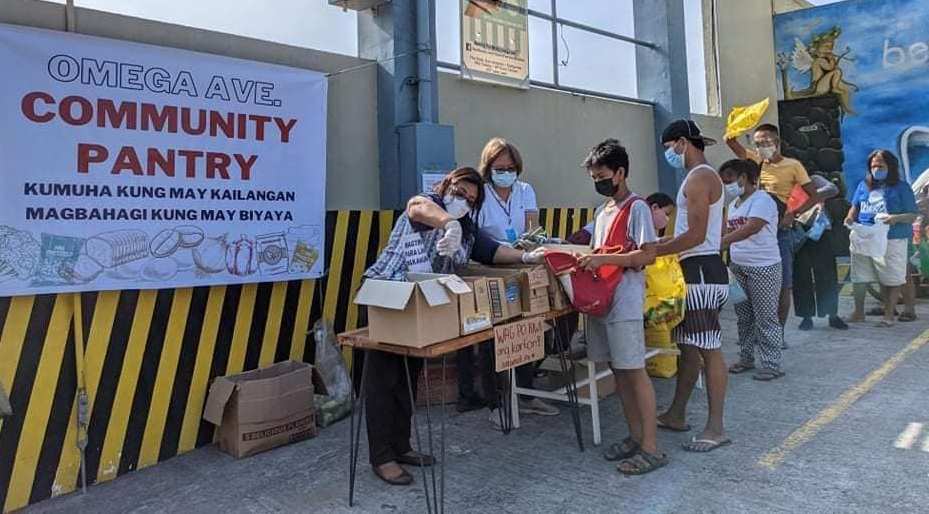

A social phenomenon bred by state abandonment
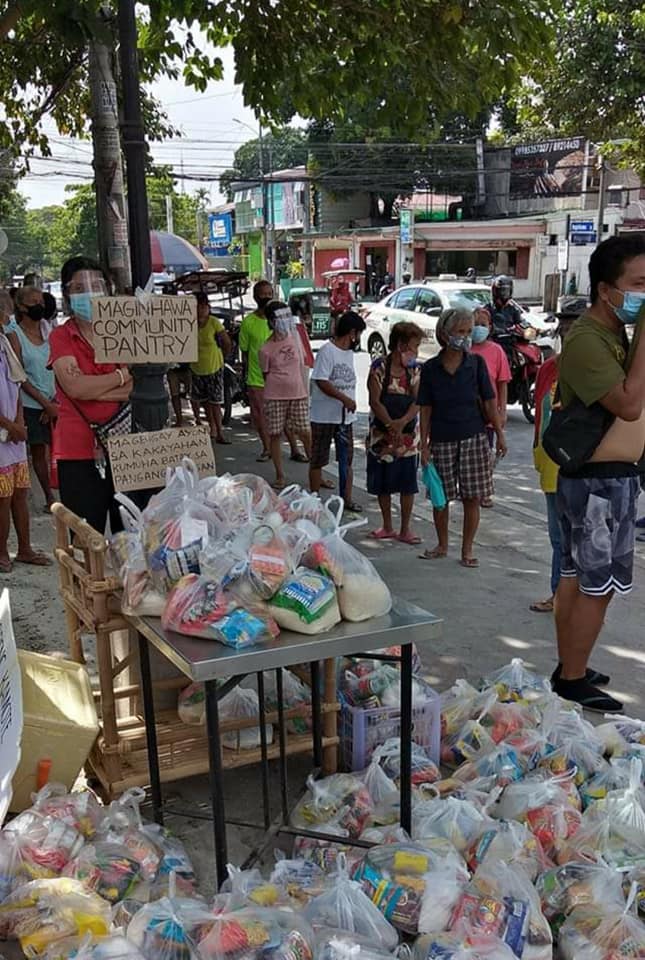
On April 14, Patreng and her little bamboo trolley of free vegetables with a signboard bearing the words, “Magbigay ayon sa kakayahan, kumuha batay sa pangangailangan (Give what you can, take what you need),” first stood on a street corner in the city with the most COVID cases and deaths in the country. Small vendors and tricycle drivers nearby have since helped Patreng repack and distribute goods as well as facilitate the daily queue of neighbors they’ve invited themselves. And just like that, a movement was born.
Within three days, PSS identified 44 community pantries nationwide with majority in NCR. As of this writing, there are 500 from as far up north as Cagayan all the way south to “DDS Country,” Davao City. PSS in its initial analysis of the community pantry calls it an “emergent agency”—an independent initiative taken by stakeholders to effect changes on their situation. Emergent collective behaviors rise when preexisting structures fail to meet people’s demands. Notably, a good chunk of the community pantries that swiftly followed Maginhawa’s example are of organized masses from marginalized sectors who initiated community kitchens and collective gardening since the first enhanced community quarantine. PSS notes that these earlier emergent agencies didn’t quite capture the people’s imagination the way community pantries have.
Although they’re not the cure to end food insecurity, the viral spread of community pantries is but a symptom of the true state of the nation: Like Patreng, Filipinos are “tired of complaining and fed up with government inaction.”

Half a piece of ginger, cups of taho and a tale of two oranges
Community pantries have been practiced in the US and other parts of the world. When COVID hit Thailand, locals installed cupboards filled with food, medicines and other necessities in public spaces in Bangkok to help one another. Called “happiness-sharing pantries,” they spread all over the country, reaching a total of 1 400 by the end of 2020. As lockdown restrictions were lifted in Thailand and stores reopened, the pantries were later abandoned.
In the Philippines, community pantries show no signs of slowing down as Duterte stays in power, hoarding public funds for his election war chest. (The original Maginhawa Community Pantry announced Monday night it will cease to be a distribution center starting today, Tuesday, April 27. It will instead be a donation center from which nearby community pantries shall be replesnished.—Ed. ) A viral element of the phenomenon is its slogan which people have adopted and translated into many different languages and dialects, my favorite being LGBTQ+ organization Bahaghari’s “Gumib luv offering ayern sa kerichinabels, gumeching vatai sa needine lustre.” More than just a catchphrase, Filipinos from all walks of life have been unified by the idea and practice of a mutual aid grounded on giving what they can and taking only what they need.
In contrast to donation drives where the same prepacked goods are given to households without taking into account household size, you have the freedom to get what your family specifically needs from a community pantry regardless of what you donate. How much one takes / gives is a non-issue. In a Bulatlat article, University of the Philippines Professor Sarah Raymundo says that community pantries defy the capitalist market because they highlight products’ utility (use value) over their monetary worth (exchange value).
This encourages people to prioritize the needs of others over their own. For instance, a resident in a resettlement area in San Jose Del Monte, Bulacan only needed a small slice of ginger, so she broke one into two pieces “para makakuha rin ang iba (so others may have as well).” In Kawit, Cavite, a taho vendor gave out free cups of his own product by a small roadside table. Inspiring passersby, they bought more cups of taho for his little pantry. Patreng also shared in the press conference how an old beggar picked up two oranges. When he was told to get more, he said two were enough to get him by for the day.
The community pantry is a utopian space where the destitute and benevolent converge, often one and the same. More than bayanihan and volunteerism, it advocates collectivism. This boggles the minds of the rich because they only understand an individualist way of life, not unlike that of a barangay captain in Los Baños, Laguna who threw a fit, accusing organizers of profiting off their pantry. His angry constituents later exposed him on social media for using personal connections to get vaccinated ahead of frontliners.

“Communist Pantry,” “just bayanihan” and other anti-people takes
Once the community pantry became a phenomenon, anyone who knows this administration damn well would’ve seen red-tagging from a mile away. Historically, emergent agencies or relief efforts that expose government incompetence are met with hostility. Last year alone, cops destroyed Sitio San Roque’s community kitchen and apprehended youth volunteers distributing food packs to impoverished communities in QC, Malate, Marikina, Bulacan, etc. Armed men killed activist Jory Porquia while conducting relief operations in Iloilo City.
According to UP Prof. Danilo Arao in an online forum on journalism ethics and community pantries, red-baiting is the “highest form of fake news” because it endangers lives. It is the state’s go-to tactic in discrediting and demonizing personalities and organizations so that hurting them is justified. Another objective of red-tagging, Arao explained, is to challenge its target/s to denounce Communist links. Sounds familiar? Mainstream media, GMA Network being the biggest offender of late, has become nothing more than a mouthpiece of a regime that persecutes people like Patreng whose only fault is facilitating change.
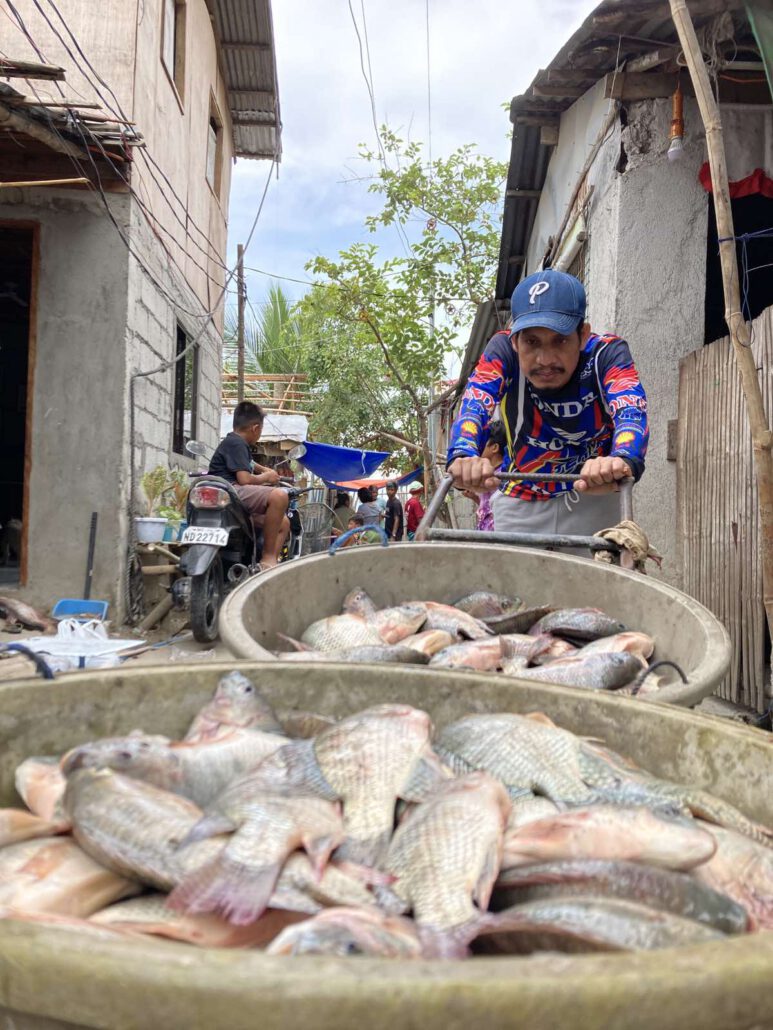
Neoliberalism has so deprived us of basic social services and turned everything into a capitalist commodity that Filipinos sharing goods among themselves has become quite the spectacle. That said, what really frightens the state is not its “phenomenal” or “bayanihan” aspect, or Patreng’s political affiliations. The community pantry is not just a place of sharing and caring but sharing and caring between the middle and lower social classes with similar traumas caused by the pandemic and exacerbated by state inutility and terrorism. Some might’ve lost jobs, others loved ones, most of them hope. Now, they find solace and strength in being able to not only take but give, whether it’s 50 kilos of fish from small fisherfolk alliance PAMALAKAYA; sacks of sweet potatoes from a farmer in Paniqui, Tarlac; or three packs of noodles from the kind balut vendor at Maginhawa. The community pantry feeds people for a day but empowers them for much longer as they continue to struggle in a society that takes jobs, loved ones and children’s lives, and thrives on widespread hunger, doom and gloom.
Community pantries as a collective refusal to not starve are a protest whether you like it or not. And it’s disturbing how Malacañang, NTF-ELCAC, some journalists and centrist liberals all sound the same: “It’s just bayanihan and should be free of any politics.” Keep calm and share gulay, they say. A bishop went as far as declaring that these pantries with their signboards will “forever erase the shame” of cardboard justice in the drug war. Great. When they’re not red-baiting whole movements, they’re whitewashing or romanticizing them. Why do we celebrate bayanihan yet balk at the idea of hopeful, empowered masses who feed one another and understand why they starve in the first place?
“Everything is political,” says PAMALAKAYA – Southern Tagalog Spokesperson Ronnel Arambulo. “Widespread hunger is a result of government inadequacy in responding to the health crisis. The national situation should not be seen as a separate picture from community pantries.”
Meanwhile, mayors have expressed support and assured organizers of their safety. A resignation was tendered. Gag orders were issued. These are little victories, indeed, but we must not be complacent. Patreng is right: She may be safe for now but entire communities are not. Believing that community pantries are red-tagged because some have given political meaning to them is only blaming the victim. It says outright, “They deserve to be red-tagged for not submitting to the status quo.” This fascist thinking is harmful to the people.
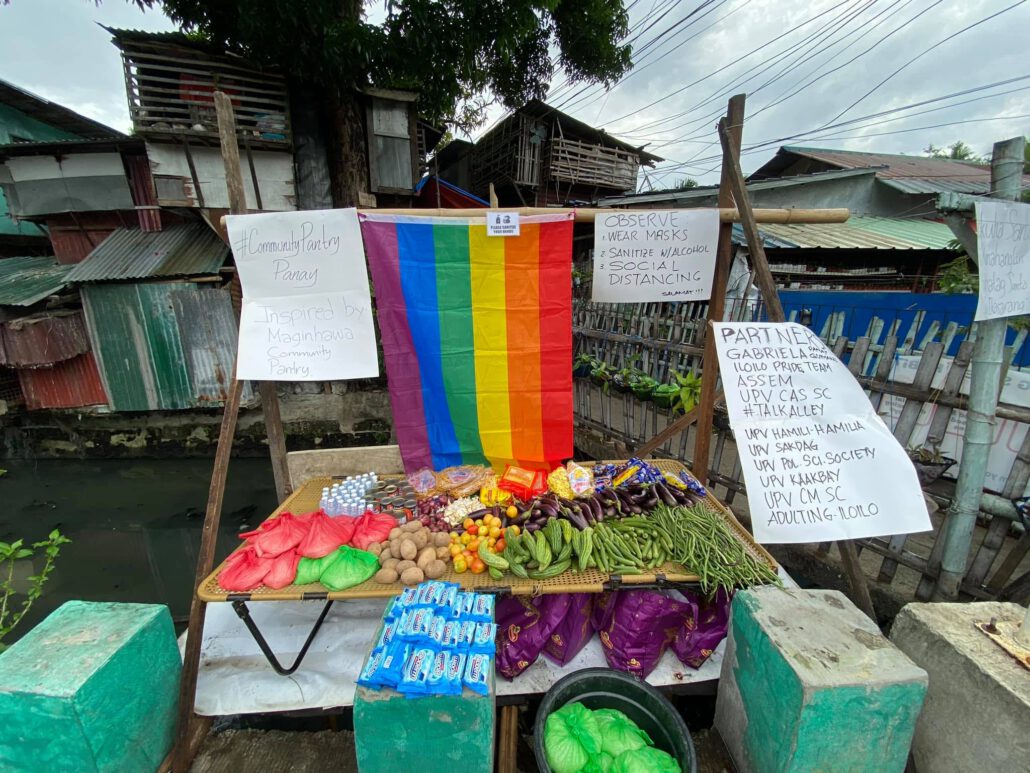

From the masses, to the masses
An organizer posted on FB about buying vegetables from a peasant in Nueva Ecija. Upon knowing they were for a community pantry, she said, “Napanood ko sa TV kanina. Nagugutom ang tao, pinapasara pa nila! Komunista raw. E ano naman? Namimigay lang naman! (I learned about it on TV. People are starving yet the government wants to close them! They call them communists. What about it? They’re only giving out food!)” After donating 200 pesos, she added, “Maganda ‘yang ginagawa ninyo. Pipila kami mamaya pero hindi na gulay ‘yung kukunin namin. Bigas sana (What you’re doing is noble. We’re going to line up at the pantry later but we won’t be getting vegetables. I hope there’s rice).”
It isn’t hard for the poor to understand and embrace the community pantry as their own because they struggle the most and have been quite vocal about their grievances. Instead of calling them “komunista,” “reklamador” or “pasaway,” Patreng listened. If the masses are not afraid to voice out their demands and work towards social change, why should we be? Let’s stop telling them what to do and as them instead what must be done. Let communities lead the way for community pantries. #
References:
Altermidya (2021, April 23). To ask or not to ask: Lessons on red-tagging & community pantry [Video]. Facebook. https://fb.watch/56UyZvIOhF/
Bolledo, J. (2021). “12-year-old boy chased by Pasay tanods loses consciousness, dies”. Rappler. Retrieved from https://www.rappler.com/nation/minor-chased-by-pasay-tanods-loses-consciousness-dies-april-2021
Chatinakrob. T. (2020). “Happiness-sharing Pantries: an effective weapon to ease hunger for the needy during the pandemic in Thailand”. Retrieved from https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/seac/2020/09/16/happiness-sharing-pantries/
Dionisio, J. et al (2021). “Contagion of Mutual Aid in the Philippines: An Initial Analysis of the Viral Community Pantry Initiative as Emergent Agency in Times of Covid-19”. Retrieved from https://philippinesociology.com/contagion-of-mutual-aid-in-the-philippines/
IBON Foundation (2021). “Joblessness worsens in February and will get worse with ECQ”. Retrieved from https://www.ibon.org/joblessness-worsens-in-february-and-will-get-worse-with-ecq-ibon/
Raymundo, S. (2021). “Community Pantry Ph: Hugpungan ng ginhawa at pag-iral ng use value”. Bulatlat. Retrieved from https://www.bulatlat.com/2021/04/22/community-pantry-ph-hugpungan-ng-ginhawa-at-pag-iral-ng-use-value/