Water you up to, Mr. President?
By Sonny Africa
Pres. Rodrigo Duterte is posturing against oligarchs again. This time, the tough talk is against corporate water giants Manila Water and Maynilad. It is a popular and justified stance – the firms make billions of pesos every year while consumers suffer expensive water and incomplete services.
The hope is that this comes from a real understanding of water as a human right where the oligarchy’s profit-seeking is seen as hindering the realization of this right. Or it might just be populist posturing against some oligarchs rather than the oligarchy.
Presidential threats
Pres. Duterte tapped into public outrage against the country’s water barons when he threatened the Ayala family and businessman Manny Pangilinan. They helm concessionaires Manila Water and Maynilad, respectively. At a speech in Malacañang, the president angrily said that Filipinos are poor because oligarchs dominate the economy.
He said he would take action against them even if this made the country a pariah in the international community and among investors. Anyway, he said: “We can start from the beginning… nandiyan naman si Villar” (Villar is there). The uneasy reference to richest Filipino Manny Villar, whose rapidly expanding PrimeWater venture makes him the country’s fastest-rising water baron, only fueled criticisms of cronyism in play.
The president also called on his audience – including senators, cabinet members, and business folks – to stop this “business of milking the people.” At the end of his short speech, everyone rose to their feet clapping.
The government seems serious about going after the two Metro Manila water concessionaires. The Solicitor General said it will pursue ‘all remedies’ to contest the water arbitral rulings that worked against the government. The justice department identified a dozen provisions making the water concession agreements (CAs) ‘onerous’. To remedy this, the finance department is drafting replacement contracts supposedly more favorable to the government and the public.
The Metropolitan Manila Waterworks and Sewerage System (MWSS) said that it will cancel the irregular 15-year extension of the CAs beyond 2022 to 2037.
Pres. Duterte himself threatened to file economic sabotage cases against the water firms and government officials involved in the disagreeable water deals. When the new water contracts are drafted, he said the water firms can basically take it or leave it. He reportedly also promised to make the lives of the Ayalas and Pangilinan “very, very, very miserable”. Among others, he threatened to slap each of the billionaires and offered this as some kind of catharsis to Filipinos.
The posturing seems to have paid off. The water firms are reportedly waiving the Php10.8 billion awarded to them by their respective international tribunals – Php3.4 billion for Maynilad and Php7.4 billion for Manila Water. The firms will also defer higher water rates scheduled for January 1, 2020 and renegotiate their contracts.
Still, water privatization
So are things, finally, all settled on the water front? Unfortunately not, if the government still sticks to its water privatization policy.
Many of the issues raised by the Duterte administration echo issues raised long ago by the Philippine mass movement (which includes many organizations now being vilified and attacked by the government). Progressive groups criticized water privatization and the CAs from the time that they were being negotiated in 1997. The Water for the People Network (WPN) meanwhile was at the forefront of civil society campaigning in 2013 against water rate hikes bloated by corporate income tax, non-implemented infrastructure projects, and a host of other irregular items.
Thus government’s apparent epiphany is welcome to the extent that it moderates corporate water profiteering. This relief is long overdue. Since the start of water privatization, water rates have increased seven-fold in the West Zone under Maynilad (573% increase) and ten-fold in the East Zone under Manila Water (871%). These rate increases far outpace inflation over that same period.
Water privatization proponents often justify expensive water with the argument: “The most expensive water is no water.” Yet beyond the catchiness, the reality is that water has become unaffordable especially for lower income families. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) suggests that water costs should not exceed 3% of household income. Yet WPN, in its studies in 2013, found poor families in Metro Manila paying as much as 7-22% of their household income for water which is so basic to survive.
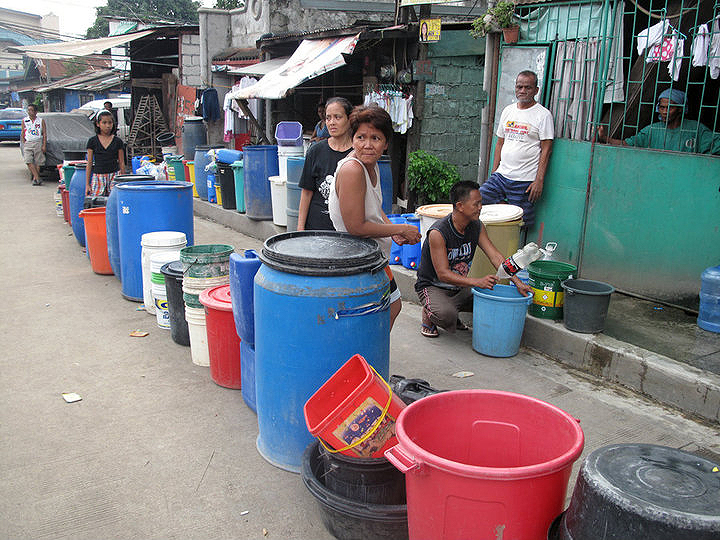

The rate increases support huge profits. In 2013, WPN noted that the two water firms had returns on investment conspicuously higher than in telecommunications, power and housing. In the last 15 years, Maynilad made around Php68 billion in profits and Manila Water some Php61 billion. In 2018 alone, the water firms raked in around Php6.6 billion in profits each. Profits are also boosted by increasing water demand from explosive Metro Manila urban over-development – meaning that the Ayala group, also a major real estate developer, profits twice over.
Water rates and the water firms’ profits would be even higher if large water rates hikes had not been stifled following citizen- and mass movement-driven protests and campaigning in 2013.
The ‘losses’ claimed by the water firms and brought to arbitration are largely about the corporate income taxes that they were disallowed from charging to water consumers. These are potentially enormous and, in the case of Manila Water, would have summed to around Php79 billion passed on to consumers from 2015-2037.
Under an unchanged framework of privatization, there are reasons to doubt whether government’s renegotiated concession agreements will be able to completely rectify these problems. The basically profit-driven approach is inappropriate and will inevitably result in contracts still unnecessarily skewed towards ensuring private profit even at the expense of social objectives.
Privatization means having public utilities and social services run by the private sector. The private sector is assumed to be inherently more efficient than the public sector and, hence, able to provide the utility or service better. The better services, it is argued, justify the more expensive prices and resulting profits.
The new renegotiated contract terms are still undetermined so it is hard to say how far two decades of expensive water and unmet sanitation targets can be corrected. Still, the global experience with water privatization may provide some clues of the prospects.
Reversing water privatization
By now, many may believe that water privatization is commonplace. Yet water privatization really only started in the 1990s and the 1997 privatization of MWSS was actually one of the first and the biggest at the time.
Privatized water is actually a minority worldwide and even in retreat.
There are around 500 large cities worldwide with a population of over one million, including the big cities in Metro Manila. Despite the wave of water privatization starting in the 1990s, 82% of these cities and their populations are actually still served by public providers.
Moreover, privatized water has been in retreat in the last decade or so. Many of the reasons for this happening abroad are familiar to Metro Manila residents: steep water rate increases, inadequate service coverage, insufficient infrastructure investment, opaqueness, and lack of accountability.
Driven by the incompatibility of the human right to water with privatization, more and more water services have been nationalized since the mid-2000s. Erstwhile privatized water services in at least 267 cities in 37 countries have returned to, or are in advanced stages of returning to, public sector hands. Nearby, this includes Jakarta in Indonesia and Selangor in Malaysia.
Elsewhere in Asia, water services are being nationalized in India and Kazakhstan. This is also happening in countries from Argentina to Uruguay in South America, from Ghana to Tanzania in Africa, from France to Sweden in Europe, and even in the US and Canada. Uruguay and the Netherlands have even gone so far as making water privatization illegal.
The nationalization of water services – or ‘remunicipalization’ as it is also called – occurs at many levels. It has been literally national in Uruguay, regional as in Argentina, city level as in Indonesia, and at the municipal or community level as in France and the US.
Water for the people
Nationalization is the real alternative to water privatization. It is the best way to ensure that water is provided as a service instead of operated as a business.
The concession agreements should be terminated as the starting point for returning Metro Manila water services to full public ownership, management and control. Government officials and the water firms should also be held accountable for over two decades of water service misdeeds.
There is a seemingly powerful counterargument to renationalizing water – why return Metro Manila water services to the government which did such a poor job of running it over two decades ago and was the reason for privatization to begin with? Privatization is flawed, it is argued, but public water is worse.
The concern is legitimate. Metro Manila water services in the 1990s certainly needed much improvement. Yet the Metro Manila and global experience these decades past are strong arguments that water should be run as a public service rather than as a business.
The drive for profits is so powerful as to override social concerns. Businesses are inherently profit-seeking and will necessarily put profits above social considerations – otherwise, they would not be businesses any more. Governments on the other hand are supposed to put social considerations above all.
Businesses will always charge a profit premium. Apparently, they will also underinvest if this will make their profit-seeking risky. In effect, water businesses will give people the water services they want as long as these are water services the business wants to give. If forced to do otherwise they will not also not hesitate to bring the State to court.
Which raises the question – how can the government improve how it runs water services? First of all, we can rule out privatization for that. The MWSS has overly relied on the water concessionaires over the past two decades. Not only has it foregone building capacity over that period, it even eroded whatever capacity it already had.
The government should seriously consider options not relying on profit-maximization. Profit-seeking underlies all variants of privatization and public-private partnerships (PPPs). There are, for instance, public-public partnerships (PUPs). These are collaborations between two public authorities on the basis of solidarity and the spirit of improving public services.
The Public Services International Research Unit (PSIRU) already reports 137 water service PUPs in around 70 countries as of 2018. PSIRU even observed that “the number of implemented PUPs largely exceeds the number of privatized contracts in the global water sector”. Such not-for-profit partnerships to build non-commercialized water and sewerage systems are the most appropriate capacity-building arrangements for realizing water as a human right.
Democratic public water
Giving citizen groups a greater role in water services can also help check corruption, abuses and inefficiency. It is already well-established that civil society organizations are vital for reflecting needs of local communities, mobilizing these to support policies and projects, and holding governments accountable. Democratic and transparent governance is not easy – but it is necessary and possible.
The political and economic interests behind neoliberalism understandably oppose nationalization of water services. This would be a direct rebuttal of their claims that corporate profit-seeking can deliver the public service that people need and deserve as a matter of human right – and on such a huge and profitable flagship privatization project as Metro Manila water no less. It is also inconsistent with the market-biased and foreign investor-friendly preferences of economic policy elites.
There is however more than enough reason to let go of the cherished neoliberal dogma that pursuing private gain through free markets is the best way to achieve optimal social outcomes. The last few months have already seen protests and uprisings around the world. Although appearing to be on disparate issues, their common root is the neoliberal economic model imposed on populations worldwide for nearly four decades. This has caused such dire consequences for so many.
In the Philippines, nationalization of water services would be a significant beachhead to advance the counterattack against neoliberalism and reclaim the economy for the people. Which is exactly why the Duterte administration, for all its posturing, is most unlikely to go in that direction. As always, sustained social and political dissent is the key to upholding the interests of the majority –indeed, more than ever in these times of neoliberal authoritarianism. #