A special report by Reynald Denver del Rosario
MANILA BAY is alive and still able to provide livelihood for thousands of fisher folk and their families, communities and environmental groups say as they continue their campaign against ongoing and future government reclamation projects on one of the country’s most important body of water.
Last year, President Rodrigo Duterte has given the green light to more than 80 billion peso worth of reclamation projects implemented by the Philippine Reclamation Authority (PRA). Despite opposition from various sectors, the government ordered a fast-tracked completion purportedly to give way to economic development and ease the metro’s traffic woes, among other reasons.
But beyond these promises of change and progress lie concrete problems faced by the environment and grassroots communities. One of the affected areas is Manila Bay, a body of water which different coastal communities rely on for their living.
With the implementation of these massive reclamation projects at full swing, affected residents face threats of losing their livelihood and communities. Since then, communities have strengthened their unity as they fight for their rights as citizens.
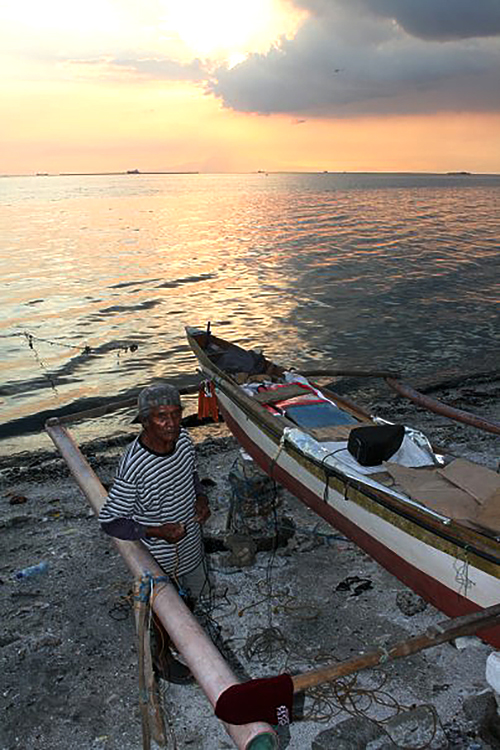

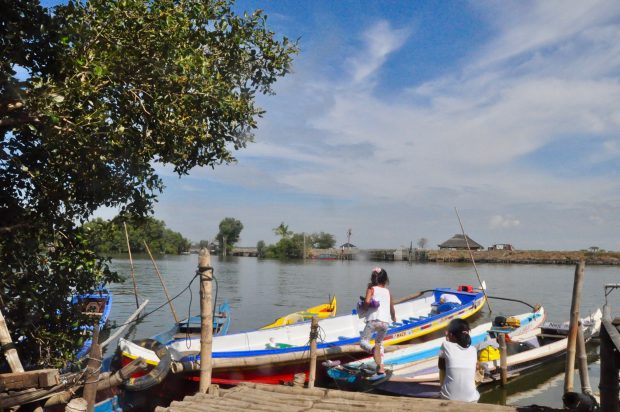
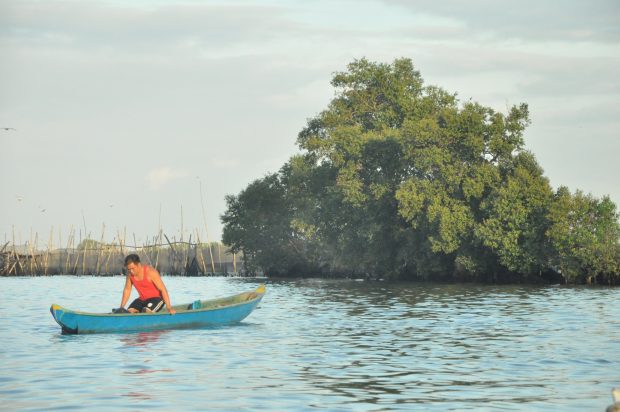
A Manila Bay fisher tending his boat after a day out trying to make a living. (Photo by R. Villanueva / Kodao)
- Manila Bay to be ravaged by eight reclamation projects
The eight ongoing and planned reclamation projects on Manila Bay include the 650-hectare Navotas Business Park reclamation project, first initiated in the 1960s but was revived during the administration of President Benigno “Noynoy” Aquino.
Manila City Mayor Joseph Estrada has also recently approved a fourth reclamation project under his term—the 419-hectare Horizon Manila project at an estimated cost of P100-billion. It involves the construction of a commercial hub composed of three new islands. This approval came two months after Estrada approved the P7-billion Manila North Harbor expansion, which will reclaim 50 hectares from the waters of the bay.
Last February, Estrada approved the New Manila Bay International Community project, a 407-hectare mixed-use commercial and tourism center proposed by UAA Kinming Development Corporation.
Estrada also upheld the Solar City project, a major entertainment hub which covers 148 hectares and approved by his predecessor Alfredo Lim.
Another reclamation intervention is the 635-hectare Las Piñas-Parañaque Coastal Bay project intended to be a residential, industrial, educational and commercial zone.
The other reclamation projects in Manila Bay include the 360-hectare project in Pasay City and the 300-hectare project in Parañaque City, a public-private partnership with a giant mall and real estate company as the private-sector partner.
These massive reclamation projects in Manila Bay are part of a larger national reclamation plan pursued by the government purportedly to further boost the country’s economy. These, however, shall come at the expense of fisherfolk and coastal communities being displaced, fisher folk and environmental groups said.
- Despite massive pollution, Manila Bay is still thriving.
The Manila Bay area is one of the Philippines’ major center of economic activity, including fishing and aquaculture activities. However, its ecosystem continues to face problems from multiple developments taking place in the area.
Pollution, over-fishing, and loss of habitats are few of the issues threatening Manila Bay, according to the Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA). Its effects include the significant degradation of the involved ecosystems and biodiversity, which eventually affects those who are dependent on it.
According to the Center for Environmental Concerns (CEC), fish are already scarce in the bay according to a public scoping undertaken by no less than the Department of Environment and National Resources (DENR).
Fisher folk challenges the claim, however, saying the DENR study is being used to justify the planned demolition of their communities and livelihood by and on the bay.
According to Pambansang Lakas ng Kilusang Mamamalakaya ng Pilipinas (PAMALAKAYA-Pilipinas), fishermen still harvest a considerable amount of fish from Manila Bay. For them, the government should rehabilitate the waters, not reclaim them.
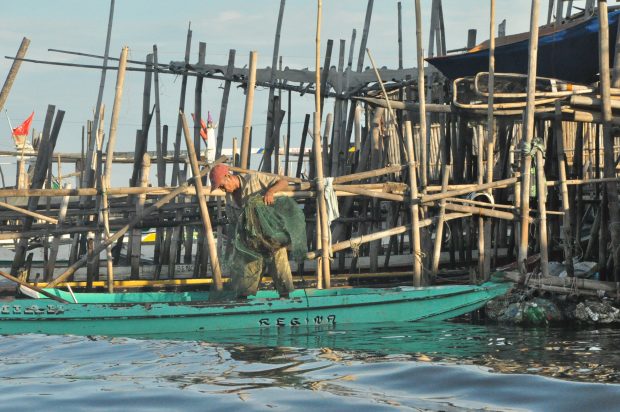
Navotas City, for example, benefits from what the waters of Manila Bay still have to offer. Dubbed as the “Fishing Capital of the Philippines” Navotas City and its residents largely depend on fishing and related industries for livelihood. Residents of Barangay Tangos in Navotas still benefit from the waters to sustain their livelihood, despite various obstacles. Fishermen harvest different kinds of seafood, including shellfish, squid and shrimp, among others.
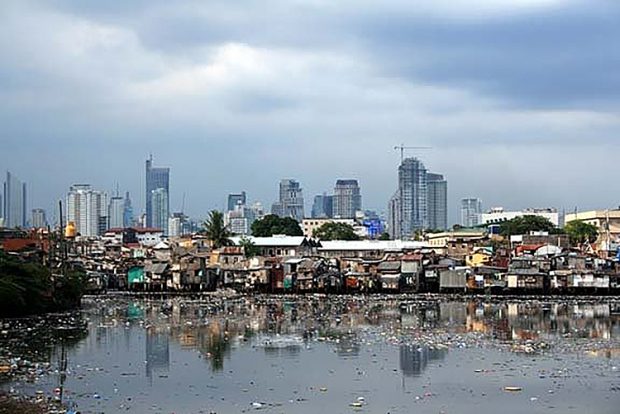

An urban poor community sits under the shadow of the towering buildings of Makati City and along the polluted Parañaque River. (Photo by Raymund B. Villanueva / Kodao)
- Waste is used as justification to displace the coastal communities.
Forty eight year old fisherman Romeo Broqueza of Barangay Tangos couldn’t hide his frustration with Manila Bay’s waste problem, saying that the issue is used against them. According to him, most of the waste came from other places and not from their community itself.
“Kung tutuusin, pwede iyang pag-usapan, kasi madali lang naman linisin iyan e. Nandiyan ang barangay, tutulong yan,” he said. “Ngayon, ginagamit nilang dahilan ‘yang kalat para paalisin kami dito.”
Residents also scored the dumping of waste in nearby communities. According to Nieves Sarcos of PAMALAKAYA, big barges continue to deliver 100 truckloads of trash to Barangay Tanza per day.
“Mataas na ang basura, parang bundok na,” she said. “Maraming nahuhulog na basura mula sa barge, tapos aanurin papunta sa amin.”
In 2008, the Supreme Court (SC) issued a writ of continuing mandamus directing 13 government agencies to clean up, rehabilitate and preserve Manila Bay in 10 years.
PAMALAKAYA claims that almost 60 percent of pollution entering Manila Bay comes from Pasig River, in which 80 percent comes from industries and commercial establishments in Metro Manila.
Manila Bay Coordinating Office executive director Antonio Gaerlan stated that wastewater from 86 percent of the 14 million households served by water concessionaires is still directly flushed out into Manila Bay. The mandatory construction of wastewater treatment facilities for all households, establishments and industries was not included in the privatization of water services under the Fidel Ramos administration with Manila Water and Maynilad Water Services.
PAMALAKAYA has condemned past and present administrations that use the SC’s order as justification to demolish fishing communities.
The fisher folk group continues to push for the rehabilitation and clean-up of Manila Bay. With its continued destruction, small-scale fishermen have experienced the trend of fish-catch depletion, from 10 to 15 kilos down to two to five kilos of average catch per day.
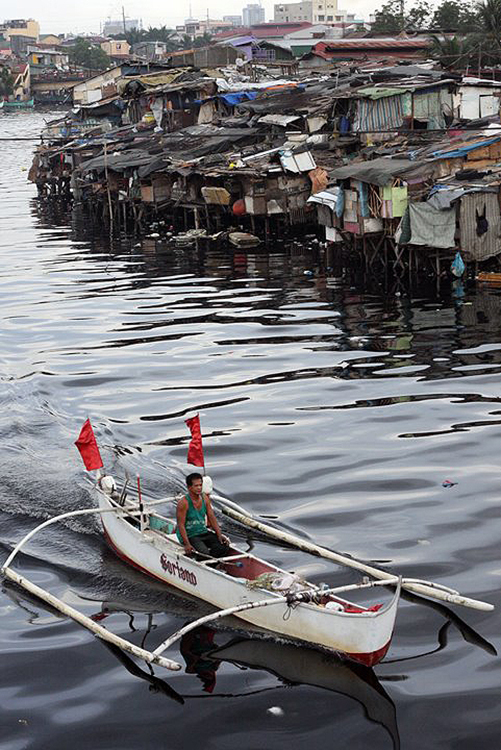

A fisher folk is heading out to Manila Bay from the Malabon River. (Photo by Raymund Villanueva / Kodao)
- Government policies threaten the livelihood of fishing communities.
According to PAMALAKAYA and Kalipunan ng Damayang Mahihirap (KADAMAY), the Navotas Business Park reclamation project would displace 20,000 fisher folk and residents across four coastal barangays in Navotas City.
The group added that fresh and affordable fish from Navotas would also become unavailable due to the displaced communities.
Markers and fences are already constructed along the shores of Barangay Tangos in preparation for the project. The fisher folk fear that the barriers would block their fishing boats from going offshore and restrict their already limited fishing activities.
According to Republic Act 10654 or “An Act to Prevent, Deter and Eliminate Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated Fishing,” small and medium fishing vessels are only allowed to operate within 10 to 15 kilometers from the coastline in municipal waters.
Fishermen are directly affected with this policy. According to them, fish of high value like tilapia and bangus cannot be found in the shallow areas; they are forced to prioritize crabs, squid, shrimp, and other small fish, which do not sell as much.
According to Broqueza, only big ships benefit from the Manila Bay since small-scale fishermen can’t go too far out to sea.
“Dati communal ‘yang Manila Bay. Malalaking isda talaga tulad ng tuna at bangus ang nahuhuli diyan, kahit ng mga maliliit na mangingisda. Kaso, ngayon, wala na,” he added.
Fish continue to dwindle because of large-scale fishing by big companies, fisherfolk say. “Pag maliliit na fishers, ‘yung sapat lang at di sobra-sobra. Yung mga negosyo kasi, sobrang mangisda,” Broqueza said.
Due to the declining fish catch, small-scale fishermen choose not to bring their fish to the Navotas Fish Port for offloading. Instead, they do business in their barangay despite earning substantially less. According to Dodong Remojo, a fisherman of 30 years, around 70 to 80 percent of the fish in the port come from Palawan anyway.
Fishermen also suffer from various violations imposed on them. There are no markers which indicate the 15-kilometer distance from the shoreline—they only estimate how far they have sailed. The ambiguity makes them vulnerable to violating the limitations stated by the law.
Patrol activities by the Philippine Coast Guard (PCG) and the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR), fisher folk say, have become a venue for corruption through the filing of various violations against small scale fisher folk.. “Hindi ka pa nga nakakalagpas, nahuli ka na e,” a resident said. Fishermen are charged from P100,000 to as high as P1.5-million, depending on the violation, including illegal equipment, lack of permit and exceeding 15 kilometers, among others.
Forty-four year-old fisherman Danilo Tulda said the officials are on patrol day and night to get the chance to yield profit from accused violations. “Araw-araw ‘yan sila, nag-aabang talaga sa laot. Kapag tumakbo ka, papuputukan ka,” Tulda said.
Rafael Sales, a fisherman for 33 years, said they were forced to pay a fine of P1.5-million after supposedly violating the law while fishing in Bataan. They were lucky as the officials eventually agreed to lower the fine to P150,000. “Kahit wala kang violation, lalagyan ka. Kaya bang bayaran ng mga mangingisda ‘yon?” Sales said.
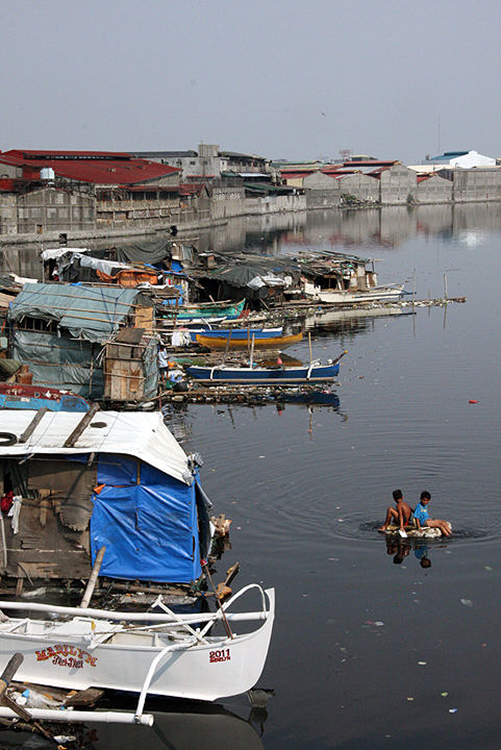

Children of fishing families practice their skills on makeshift rafts on the Malabon River. (Photo by Raymund Villanueva / Kodao)
- Damage has been done by the reclamation projects, and will continue to do so.
CEC’s Lia Alonzo cites previous reclamation projects as contributory to more hazards on the bay, such as the one which gave way to a giant mall by the bay and even earlier ones such as the Cultural Center of the Philippines complex undertaken under the Ferdinand Marcos regime.
Geologists said further reclamation projects pose greater danger as the area stands on top of a fault line. The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) already said that Metro Manila is overdue for a strong magnitude 7.2 earthquake from the West Valley Vault that traverses Metro Manila from north to south.
Alonzo cites the flaws of DENR’s issuance of the environmental compliance certificate (ECC) under the Philippine Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) as one of the factors.
The ECC is an issued document after a positive review that a project meets environmental laws and policies and certifying that the proposed project will not cause significant negative environmental impact. In practice, however, issuance of the said document favors the reclamation projects and its proponents.
According to CEC, the government failed to evaluate larger domino effects of the reclamation projects to different communities. “Nakikita natin na may mga lugar na maaapektuhan ng projects pero di na sakop ng EIS,” Alonzo said.
PRA said that engineering solutions will be applied to prevent potential damage.
CEC, however, stated that such processes are both expensive and are not foolproof. CEC maintains their stance of rehabilitating the Manila Bay under the mandamus issued by the SC. Reclamation, they say, will further destroy the already damaged ecosystems and shall affect many fisher folks.
“It is not enough reason to say na wala naman nang buhay diyan, kaya hayaan na lang nating i-reclaim,” Alonzo said. “Para sa mga mangingisda, di pa huli ang lahat para ma-rehabilitate ang Manila Bay.” #