Philippine health recovery not a priority for Duterte administration
Deliberations on the proposed Php4.5-trillion General Appropriations Act (GAA) for 2021 have begun. This budget will be crucial for the Philippines to fast track recovery from the worst health and economic crisis in its history because of COVID-19. But it is not at all about health recovery as the Duterte administration hypes.
In the National Expenditure Program (NEP) for 2021 submitted to Congress, the government actually defunds areas that are vital to boost the public health system in the time of a pandemic. These include those for disease surveillance, health infrastructure, and human resource capacity building. Despite the glaring health and economic needs exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic, the NEP for 2021 reflects how the government sticks to its old priorities such as transport infrastructure and defense, which are not what the situation urgently requires.
Making the health system weaker
The effect of COVID-19 on the health and livelihoods of the Filipino people is more severe compared to other nations. While countries around the world are starting to recover from the pandemic, the Philippines has the most total and new COVID-19 cases and the most deaths per million population in East Asia.
COVID-19 is stretching the health system’s capacity and the vaccine for the coronavirus is still far from the people’s reach. It is only rational and urgent to ensure that resources to further enhance and capacitate the country’s health system are made available. However, the government is not prioritizing this.
Bayanihan 2, a stimulus package aiming to cushion the effects of the pandemic, allots only Php30.5 billion for health-related responses to COVID such as tracing, treatment, support for health workers, health facilities, and pandemic research. There is also a Php10-billion standby fund for testing, which is paltry according to health advocates.
The proposed 2021 budget for the Department of Health meanwhile has been increased from Php104 billion in 2020 to Php131.7 billion in 2021 or a Php27.7-billion hike. But allotments for some of the most essential programs for health recovery have been slashed.
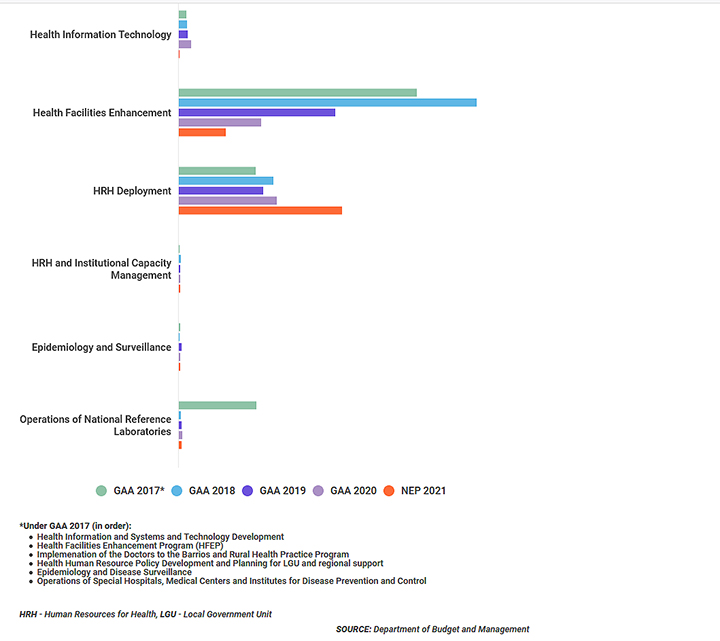
Selected Health Programs, 2017-2021
The budget for the Epidemiology and Surveillance program, which is important to control the spread of diseases through timely data and research, was halved in 2020 – from Php263 million in 2019 to Php116 million this year. A larger budget would clearly have helped strengthen preventive measures versus COVID-19 in the country at the beginning of the year when the first cases emerged. Yet despite the proven importance of this program, the government even proposes to reduce it further to Php113 million in 2021.
The proposed budget allocation for the Health Facilities Enhancement Program (HFEP), which ensures the maintenance and quality of public healthcare facilities, also decreases this year. HFEP is actually being allocated lower and lower budgets each year as hospitals are obliged to generate their own income to fund infrastructure-building and maintenance. From an Php8.4 billion budget for HFEP in 2020, the proposed budget for 2021 is only Php4.8 billion, or almost 50% less than its current budget.
The National Reference Laboratories are vital in detecting and testing COVID-19 cases and other emerging diseases. But the proposed budget for these decreases from the present Php326 million to Php289 million.
Even though one of the main issues during this pandemic is poor data management and reporting by the DOH, the proposed budget for Health Information Technology drops massively from Php1.2 billion in 2020 – which it failed to use properly – to Php97 million, or a 92% decrease.
The proposed budget allocation for Human Resource for Health (HRH) deployment increases, but the program that ensures that the health workforce is equipped with proper training and knowledge to deal with different medical situations is decreased. The budget for HRH Institutional and Capacity Management has been cut by Php15 million.
The DOH’s COVID-19 specific programs – the Php4.2 billion Health System Enhancement to Address and Limit COVID-19 and the Php1 billion Philippines COVID-19 Emergency Response Project – are mere drops in the country’s budget bucket.
What government cares for
The Duterte administration’s proposed budget for 2021 shows how little it cares for the health and socioeconomic recovery of the Filipino people. The biggest chunk of the proposed 2021 budget goes to the Php1.1 trillion “Build, Build, Build” program taking up 24% of the total budget. Only a tiny fraction of this goes to health infrastructure with the DOH getting just Php2.3 billion or barely one-fifth of one percent (0.2%) of total infrastructure spending.
Many of the infrastructure projects lined up – such as big-ticket railways and roads funded with China and Japan loans – are not as urgently needed as facilities for health and more direct measures to support the socioeconomic recovery of distressed households and small businesses.
The government is apparently only willing to spend Php203.1 billion on its so-called universal health care program including to respond to the pandemic – this is just 4.5% of the total proposed budget for 2021. As it is, the Php1.1 trillion infrastructure budget is almost 5 ½ times larger.
The proposed budget for the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) is Php667.3 billion or over five times that of the DOH. The government will allocate Php7.6 billion for primary roads’ maintenance and repair alone which is almost three times the size of the DOH budget for the COVID-19 vaccine, at only Php2.4 billion.
The DOH’s proposed Php203.1 billion budget – even including the budget for PhilHealth – ranks only 5th among department budgets in 2021. This is because, amid the unprecedented public health emergency, the DOH’s proposed 2021 budget is only a Php25.4 billion increase from the GAA this year.
The DPWH gets a much bigger Php228.4 billion increase to Php667.3 billion, as does the Department of National Defense (DND) which gets a Php29.4 billion increase to Php209.1 billion. The military and police forces will still be receiving more funds than the health sector.
The Duterte administration’s proposed 2021 budget bares how it is not changing its priorities despite the marked worsening of the Philippine health situation. Even before the COVID-19 pandemic, infrastructure has been consistently a priority over the health sector which, if anything, is even being distorted and privatized. The people’s health and strengthening the public health system are among the most immediate areas needing attention which, apparently, the administration simply refuses to give. #